Author:
nice01qc
Time :
Time :
2-3查找树 -> 红黑树
简单的介绍2-3查找树和红黑树的原理和实现细节…
平衡二叉树:在二叉树的基础上,使树的高度最低,达到平衡
-
红链接均为左链接;
-
没有任何一个节点同时和两条链接相连;
-
该树是完美黑色平衡的,即任意空链接到根节点的路径上的黑链接数量相同。
// node
private class Node {
Key key;
Value val;
Node left, right;
int N;
boolean color;
public Node(Key key, Value val, int N, boolean color){
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.N = N;
this.color = color;
}
}
2-3树:
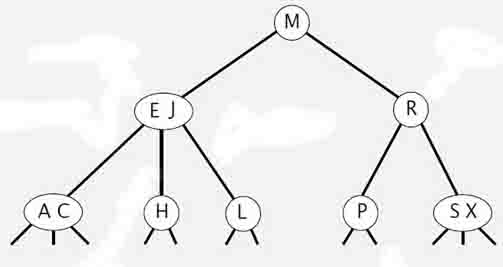
红黑树:
左旋:
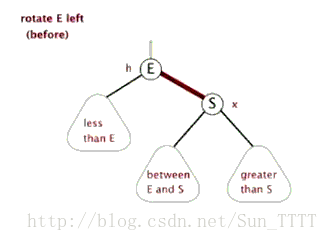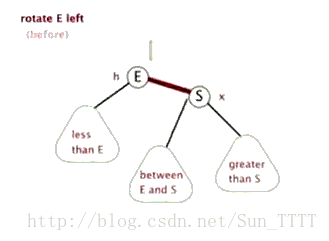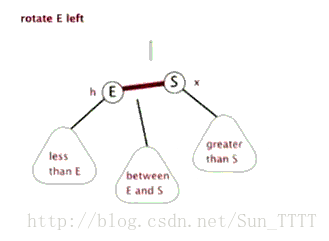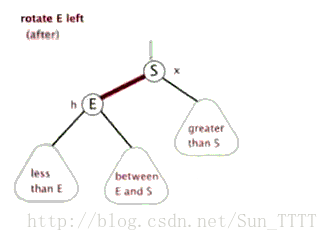
Node rotateLeft(Node h){ // 此旋转交换颜色
Node x = h.right;
h.right = x.left;
x.left = h;
boolean tmp = x.color;
x.color = h.color;
h.color = tmp;
x.N = h.N;
h.N = 1 + size(h.left) + size(h.right);
return x;
}
右旋:
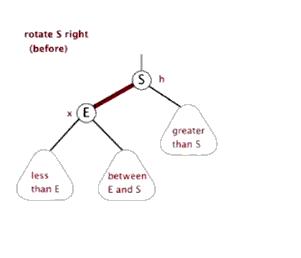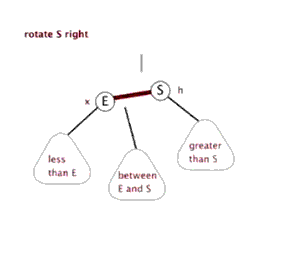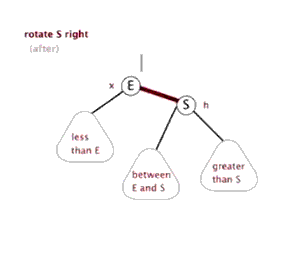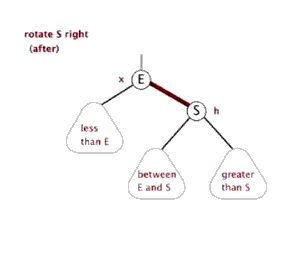
Node rotateRight(Node h){ // 此旋转交换颜色
Node x = h.left;
h.left = x.right;
x.right = h;
boolean tmp = x.color;
x.color = h.color;
h.color = tmp;
x.N = h.N;
h.N = 1 + size(h.left) + size(h.right);
return x;
}
颜色反转:
void flipColor(Node h){
h.color = !h.color;
h.left.color = !h.left.color;
h.right.color = !h.right.color;
}
插入算法:
public void put(Key key, Value val){
root = put(root, key, val);
root.color = BLACK;
}
public Node put(Node h, Key key, Value val){
if (h == null) return new Node(key,val,1,RED);
int cmp = key.compareTo(h.key);
if (cmp < 0) h.left = put(h.left, key, val);
if (cmp > 0) h.right = put(h.right, key, val);
if (cmp == 0) h.val = val;
// 恢复颜色
if (isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) h = rotateLeft(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateright(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColor(h);
h.N = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;
return h;
}
普通的二叉树删除:
-
如果删除的是叶节点,可以直接删除;
-
如果被删除的元素有一个子节点可以将子节点直接移到被删除元素的位置;
-
如果有两个子节点,这时候就可以把被删除元素的右支的最小节点(被删除元素右支的最左边的节点)和被删除元素互换,我们把被删除元素右支的最左边的节点称之为后继节点(后继元素),然后在根据情况1或者情况2进行操作。
在此基础进行改进,使删除后颜色恢复颜色平衡
他与普通二叉树删除区别是:删除元素需要保证整体颜色,需要满足那第三条定义,前两条通过平衡可以回复。
因此,为了保证在删除时,防止出现全黑而无法操作删除时(防止节点的左节点和左节点的左节点连续为黑,以及节点的右节点和右节点的左节点同时为黑),而使被删除的节点和其父节点之中至少存在一个颜色为红色,这样使删除更加简单。因此,需要从根节点开始就进行判断,及时进行逆向颜色恢复。
由于删除需要删除最小节点,因此顺便可以写出删除最大和最小的函数;
// 删除最小键函数 public void deleteMin(){ // 删除最小键开放接口 if (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right)){ // 此处为了保证最后平衡时,根节点任然为黑色 root.color = ture; // red } root = deleteMin(root); if (!isEmpty()) root.color = false; // 此处已经没必要了,上面已经有保证了 } private Node deleteMin(Node h){ // if (isRed(h.right)) h = rotateLeft(h); // moveRedLeft 已经规避了这种情况 if (h.left == null) return null; if (!isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = moveRedLeft(h); h.left = deleteMin(h.left); return balance(h); } // 删除最大键 public void deleteMax() { if (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right)) root.color = RED; // 同上 root = deleteMax(root); if (!isEmpty()) root.color = BLACK; } private Node deleteMax(Node h) { if (isRed(h.left)) h = rotateRight(h); // 为了防止删除根节点时,却还有左节点 if (h.right == null) return null; if (!isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left)) h = moveRedRight(h); h.right = deleteMax(h.right); return balance(h); }private Node moveRedLeft(Node h){ flipColor(h); if (isRed(h.right.left)){ // 为了防止 h 再恢复颜色时,没照顾到h.right.left,具体见下图 h.right = rotateRight(h.right); h = rotateLeft(h); } return h; } private Node moveRedRight(Node h) { flipColors(h); if (isRed(h.left.left)) { h = rotateRight(h); flipColors(h); } return h; } private Node balance(Node h) { // assert (h != null); if (isRed(h.right)) h = rotateLeft(h); if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateRight(h); if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColors(h); h.size = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1; return h; }
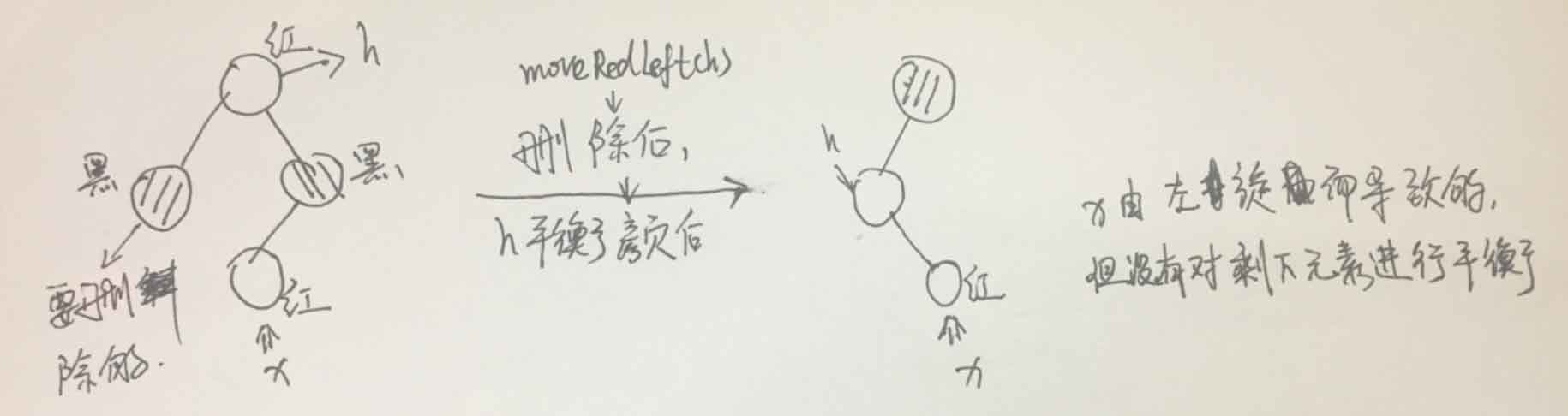
// 删除操作:
public void delete(Key key) {
if (!contains(key)) return; // 感觉可以不要,效率更高
if (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right))
root.color = RED;
root = delete(root, key);
if (!isEmpty()) root.color = BLACK;
}
private Node delete(Node h, Key key) {
if (key.compareTo(h.key) < 0) {
if (!isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left)) // 防止左边为全黑的情况
h = moveRedLeft(h);
h.left = delete(h.left, key);
}
else {
if (isRed(h.left)) // 防止被删除的元素存在左节点而没有右节点,使左节点丢失
h = rotateRight(h);
if (key.compareTo(h.key) == 0 && (h.right == null)) // 删除最后落单的元素
return null;
if (!isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left)) // 到此步,说明元素在节点右支,防止右边全黑情况
h = moveRedRight(h);
if (key.compareTo(h.key) == 0) {
Node x = min(h.right);
h.key = x.key;
h.val = x.val;
h.right = deleteMin(h.right);
}
else h.right = delete(h.right, key);
}
return balance(h);
}
其实Java集合中的TreeMap中红黑树实现就很经典,结构很清晰,代码很优美,一下对此进行介绍(其关键代码为左旋、右旋、插入结构恢复、删除结构回复)
// 节点
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
//......
}
// 左旋
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry<K,V> r = p.right;
p.right = r.left;
if (r.left != null)
r.left.parent = p;
r.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = r;
else if (p.parent.left == p)
p.parent.left = r;
else
p.parent.right = r;
r.left = p;
p.parent = r;
}
}
// 右旋
private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry<K,V> l = p.left;
p.left = l.right;
if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p;
l.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = l;
else if (p.parent.right == p)
p.parent.right = l;
else p.parent.left = l;
l.right = p;
p.parent = l;
}
}
// 插入后修复
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {
x.color = RED;
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
} else {
Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
root.color = BLACK;
}
// 使x可以被删除
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateRight(sib);
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
} else { // symmetric
Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateLeft(sib);
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK);
}
// 中序遍历用到的
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
参考资源:
http://blog.csdn.net/sun_tttt/article/details/65445754